Understanding CMC Injury: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, And Prevention
CMC injury, or carpometacarpal injury, is a condition that affects the base of the thumb and can lead to significant pain and dysfunction. This injury is particularly common among athletes and individuals who engage in repetitive hand activities. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for CMC injuries is crucial for effective management and recovery. In this article, we will delve deeply into CMC injury, providing valuable insights and information that you need to know.
Whether you are an athlete, a healthcare provider, or simply someone looking to understand more about thumb injuries, this comprehensive guide will cover all aspects of CMC injuries. We will explore the anatomy involved, the mechanisms of injury, common symptoms, and the best treatment options available. Additionally, we will discuss preventive measures to help you avoid such injuries in the future.
With a focus on expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness, we aim to provide you with reliable information that you can use to understand CMC injuries better. Let’s dive into this important topic and equip ourselves with knowledge that could make a difference in our lives.
Table of Contents
- Understanding CMC Injury
- Anatomy of the Thumb
- Causes of CMC Injury
- Symptoms of CMC Injury
- Diagnosis of CMC Injury
- Treatment Options for CMC Injury
- Preventive Measures for CMC Injury
- Conclusion
Understanding CMC Injury
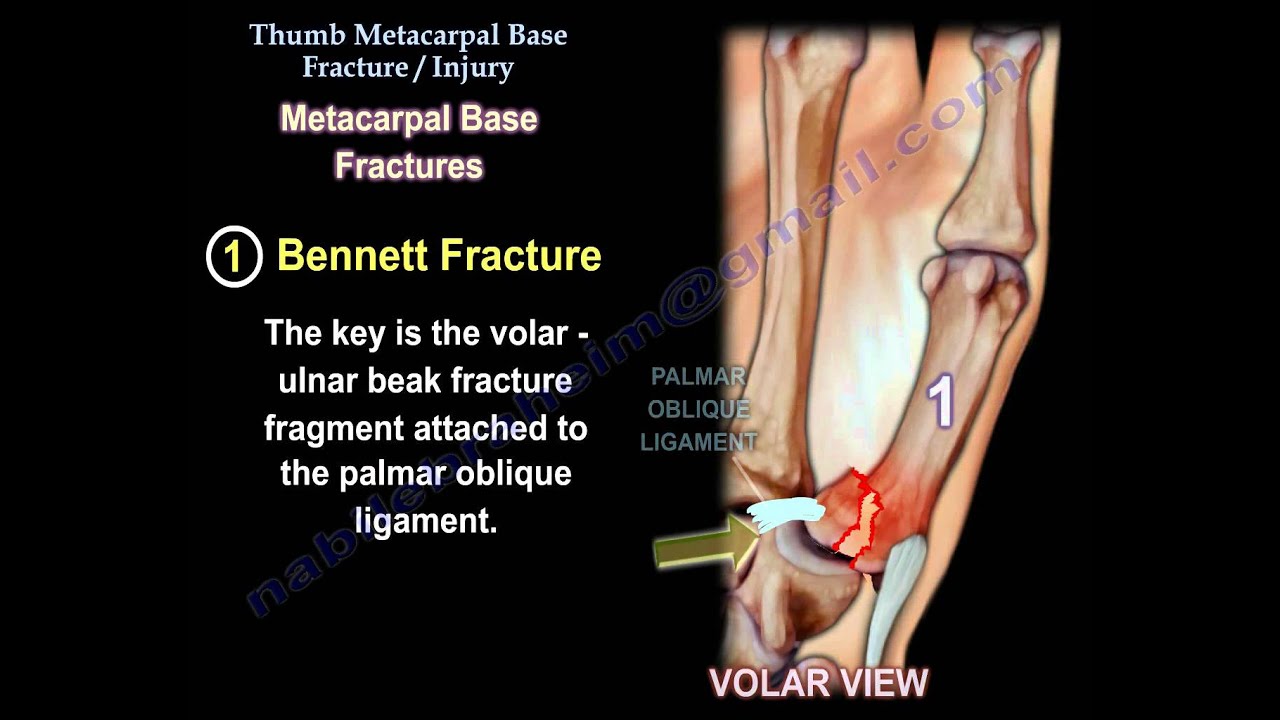
CMC injury, specifically referring to injuries at the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb, can result from various factors, including acute trauma or chronic overuse. This joint plays a crucial role in thumb mobility and grip strength, making it essential for daily tasks.
Injuries to the CMC joint can be classified into two main types: acute injuries, such as fractures or dislocations, and chronic injuries, often resulting from repetitive stress or degenerative conditions like osteoarthritis. Understanding the underlying causes and mechanisms of injury is vital for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Anatomy of the Thumb
The thumb consists of several bones, ligaments, and tendons that work together to provide a wide range of motion and strength. The carpometacarpal joint connects the wrist to the thumb, allowing for the unique opposable nature of the thumb.
- Bones: The CMC joint is formed by the trapezium bone in the wrist and the base of the first metacarpal bone.
- Ligaments: Several ligaments stabilize the CMC joint, providing support during movement.
- Tendons: Tendons from various muscles control thumb movements, enabling actions such as gripping and pinching.
Causes of CMC Injury
The causes of CMC injuries can vary, but they generally fall into two categories: acute trauma and chronic overuse.
Acute Trauma
Acute injuries often occur due to sudden impacts or falls, leading to fractures or dislocations. Common scenarios include:
- Sports accidents (e.g., falling during a game)
- Workplace injuries involving heavy lifting
- Motor vehicle accidents
Chronic Overuse
Chronic injuries usually develop over time due to repetitive stress on the CMC joint. Common activities that may lead to overuse injuries include:
- Repetitive gripping or pinching (e.g., in certain occupations or sports)
- Frequent use of hand tools
- Degenerative conditions such as arthritis
Symptoms of CMC Injury
Individuals with a CMC injury may experience a range of symptoms, which can vary in severity. Common symptoms include:
- Pain at the base of the thumb, especially during movement
- Swelling and tenderness around the CMC joint
- Decreased grip strength
- Difficulty performing daily tasks, such as opening jars or holding objects
Diagnosis of CMC Injury
Diagnosing a CMC injury typically involves a thorough physical examination and imaging studies. Healthcare providers may utilize the following methods:
- Physical examination to assess pain, swelling, and range of motion
- X-rays to identify fractures or dislocations
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) for a detailed view of soft tissue injuries
Treatment Options for CMC Injury
Treatment for a CMC injury will depend on the severity of the injury. Options may include:
Conservative Treatment
- Rest and immobilization using a splint or brace
- Ice therapy to reduce swelling and pain
- Physical therapy to strengthen the surrounding muscles
Surgical Treatment
In cases of severe injuries, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options can include:
- Joint reconstruction or fusion
- Arthroplasty, or joint replacement
Preventive Measures for CMC Injury
Preventing CMC injuries is essential, especially for individuals engaged in high-risk activities. Here are some preventive measures:
- Warming up and stretching before physical activities
- Using ergonomic tools to reduce strain on the hands
- Taking breaks during repetitive tasks to avoid overuse
Conclusion
CMC injury can significantly impact one’s quality of life, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can lead to better management and recovery. Remember to take preventive measures to protect your hands and seek prompt medical attention if you experience any symptoms.
We encourage you to share your thoughts in the comments section below and explore our other articles for more health-related information.
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back here soon for more insightful articles!
Texas Longhorns News: The Latest Updates And Insights On The Longhorns
Polly Holliday: A Journey Through Her Life And Career
My Portfolio: A Comprehensive Guide To Showcasing Your Work